Headless Chrome 入門

摘要
在 Chrome 59 中開始搭載 Headless Chrome。這是一種在 無需顯示 的環境下運行 Chrome 瀏覽器的方式。從本質上來說,就是不用 chrome 瀏覽器來運行 Chrome 的功能!它將 Chromium 和 Blink 渲染引擎提供的所有現代 Web 平台的功能都帶入了命令行。
它有什麼用?
無需顯示 的瀏覽器對於自動化測試和不需要可視化 UI 界面的伺服器環境是一個很好的工具。例如,你可能需要對真實的網頁運行一些測試,創建一個 PDF,或者只是檢查瀏覽器如何呈現 URL。
注意: Mac 和 Linux 上的 Chrome 59 都可以運行無需顯示模式。對 Windows 的支持將在 Chrome 60 中提供。要檢查你使用的 Chrome 版本,請在瀏覽器中打開
chrome://version。
開啟 無需顯示 模式(命令行界面)
開啟 無需顯示 模式最簡單的方法是從命令行打開 Chrome 二進位文件。如果你已經安裝了 Chrome 59 以上的版本,請使用 --headless 標誌啟動 Chrome:
chrome
--headless # Runs Chrome in headless mode.
--disable-gpu # Temporarily needed for now.
--remote-debugging-port=9222
https://www.chromestatus.com # URL to open. Defaults to about:blank.
注意:目前你仍然需要使用
--disable-gpu標誌。但它最終會不需要的。
chrome 二進位文件應該指向你安裝 Chrome 的位置。確切的位置會因平台差異而不同。當前我在 Mac 上操作,所以我為安裝的每個版本的 Chrome 都創建了方便使用的別名。
如果您使用 Chrome 的穩定版,並且無法獲得測試版,我建議您使用 chrome-canary 版本:
alias chrome="/Applications/Google Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google Chrome"
alias chrome-canary="/Applications/Google Chrome Canary.app/Contents/MacOS/Google Chrome Canary"
alias chromium="/Applications/Chromium.app/Contents/MacOS/Chromium"
在這裡下載 Chrome Cannary。
命令行的功能
在某些情況下,你可能不需要以腳本編程的方式操作 Headless Chrome。可以使用一些有用的命令行標誌來執行常見的任務。
列印 DOM
--dump-dom 標誌將列印 document.body.innerHTML 到標準輸出:
chrome --headless --disable-gpu --dump-dom https://www.chromestatus.com/
創建一個 PDF
--print-to-pdf 標誌將頁面轉出為 PDF 文件:
chrome --headless --disable-gpu --print-to-pdf https://www.chromestatus.com/
截圖
要捕獲頁面的屏幕截圖,請使用 --screenshot 標誌:
chrome --headless --disable-gpu --screenshot https://www.chromestatus.com/
# Size of a standard letterhead.
chrome --headless --disable-gpu --screenshot --window-size=1280,1696 https://www.chromestatus.com/
# Nexus 5x
chrome --headless --disable-gpu --screenshot --window-size=412,732 https://www.chromestatus.com/
使用 --screenshot 標誌運行 Headless Chrome 將在當前工作目錄中生成一個名為 screenshot.png 的文件。如果你正在尋求整個頁面的截圖,那麼會涉及到很多事情。來自 David Schnurr 的一篇很棒的博文已經介紹了這一內容。請查看 使用 headless Chrome 作為自動截屏工具。
REPL 模式 (read-eval-print loop)
--repl 標誌可以使 Headless Chrome 運行在一個你可以使用瀏覽器評估 JS 表達式的模式下。執行下面的命令:
$ chrome --headless --disable-gpu --repl https://www.chromestatus.com/
[0608/112805.245285:INFO:headless_shell.cc(278)] Type a Javascript expression to evaluate or "quit" to exit.
>>> location.href
{"result":{"type":"string","value":"https://www.chromestatus.com/features"}}
>>> quit
在沒有瀏覽器界面的情況下調試 Chrome
當你使用 --remote-debugging-port=9222 運行 Chrome 時,它會啟動一個支持 DevTools 協議的實例。該協議用於與 Chrome 進行通信,並且驅動 Headless Chrome 瀏覽器實例。它也是一個類似 Sublime、VS Code 和 Node 的工具,可用於應用程序的遠程調試。#協同效應
由於你沒有瀏覽器用戶界面可用來查看網頁,請在另一個瀏覽器中輸入 http://localhost:9222,以檢查一切是否正常。你將會看到一個 可檢查的 頁面的列表,可以點擊它們來查看 Headless Chrome 正在呈現的內容:
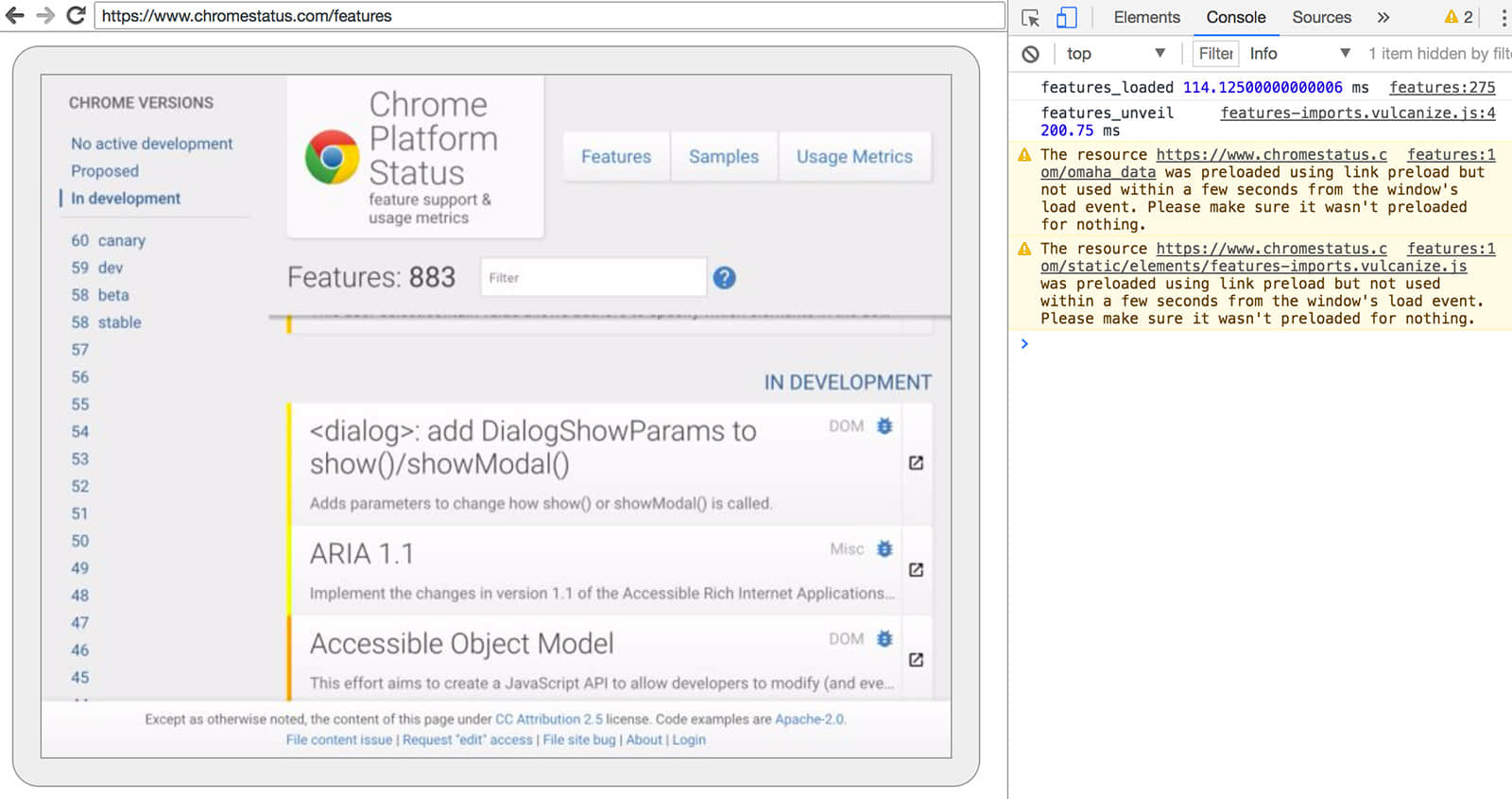
DevTools 遠程調試界面
從這裡,你就可以像往常一樣使用熟悉的 DevTools 來檢查、調試和調整頁面了。如果你以編程方式使用 Headless Chrome,這個頁面也是一個功能強大的調試工具,用於查看所有通過網路與瀏覽器交互的原始 DevTools 協議命令。
使用編程模式 (Node)
Puppeteer 庫 API
Puppeteer 是一個由 Chrome 團隊開發的 Node 庫。它提供了一個高層次的 API 來控制無需顯示版(或 完全版)的 Chrome。它與其他自動化測試庫,如 Phantom 和 NightmareJS 相類似,但是只適用於最新版本的 Chrome。
除此之外,Puppeteer 還可用於輕鬆截取屏幕截圖,創建 PDF,頁面間導航以及獲取有關這些頁面的信息。如果你想快速地自動化進行瀏覽器測試,我建議使用該庫。它隱藏了 DevTools 協議的複雜性,並可以處理諸如啟動 Chrome 調試實例等繁冗的任務。
安裝:
yarn add puppeteer
例子 - 列印用戶代理:
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
(async() => {
const browser = await puppeteer.launch();
console.log(await browser.version());
browser.close();
})();
例子 - 獲取頁面的屏幕截圖:
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
(async() => {
const browser = await puppeteer.launch();
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://www.chromestatus.com', {waitUntil: 'networkidle'});
await page.pdf({path: 'page.pdf', format: 'A4'});
browser.close();
})();
查看 Puppeteer 的文檔,了解完整 API 的更多信息。
CRI 庫
chrome-remote-interface 是一個比 Puppeteer API 更低層次的庫。如果你想要更接近原始信息和更直接地使用 DevTools 協議的話,我推薦使用它。
啟動 Chrome
chrome-remote-interface 不會為你啟動 Chrome,所以你要自己啟動它。
在前面的 CLI 章節中,我們使用 --headless --remote-debugging-port=9222 手動啟動了 Chrome。但是,要想做到完全自動化測試,你可能希望從你的應用程序中啟動 Chrome。
其中一種方法是使用 child_process:
const execFile = require('child_process').execFile;
function launchHeadlessChrome(url, callback) {
// Assuming MacOSx.
const CHROME = '/Applications/Google Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google Chrome';
execFile(CHROME, ['--headless', '--disable-gpu', '--remote-debugging-port=9222', url], callback);
}
launchHeadlessChrome('https://www.chromestatus.com', (err, stdout, stderr) => {
...
});
但是如果你想要在多個平台上運行可移植的解決方案,事情會變得很棘手。請注意 Chrome 的硬編碼路徑:
使用 ChromeLauncher
Lighthouse 是一個令人稱奇的網路應用的質量測試工具。Lighthouse 內部開發了一個強大的用於啟動 Chrome 的模塊,現在已經被提取出來單獨使用。chrome-launcher NPM 模塊 可以找到 Chrome 的安裝位置,設置調試實例,啟動瀏覽器和在程序運行完之後將其殺死。它最好的一點是可以跨平台工作,感謝 Node!
默認情況下,chrome-launcher 會嘗試啟動 Chrome Canary(如果已經安裝),但是你也可以更改它,手動選擇使用的 Chrome 版本。要想使用它,首先從 npm 安裝:
yarn add chrome-launcher
例子 - 使用 chrome-launcher 啟動 Headless Chrome:
const chromeLauncher = require('chrome-launcher');
// Optional: set logging level of launcher to see its output.
// Install it using: yarn add lighthouse-logger
// const log = require('lighthouse-logger');
// log.setLevel('info');
/**
* Launches a debugging instance of Chrome.
* @param {boolean=} headless True (default) launches Chrome in headless mode.
* False launches a full version of Chrome.
* @return {Promise<ChromeLauncher>}
*/
function launchChrome(headless=true) {
return chromeLauncher.launch({
// port: 9222, // Uncomment to force a specific port of your choice.
chromeFlags: [
'--window-size=412,732',
'--disable-gpu',
headless ? '--headless' : ''
]
});
}
launchChrome().then(chrome => {
console.log(`Chrome debuggable on port: ${chrome.port}`);
...
// chrome.kill();
});
運行這個腳本沒有做太多的事情,但你應該能在任務管理器中看到啟動了一個 Chrome 的實例,它載入了頁面 about:blank。記住,它不會有任何的瀏覽器界面,我們是無需顯示的。
為了控制瀏覽器,我們需要 DevTools 協議!
檢索有關頁面的信息
警告: DevTools 協議可以做一些有趣的事情,但是起初可能有點令人生畏。我建議先花點時間瀏覽 DevTools 協議查看器。然後,轉到
chrome-remote-interface的 API 文檔,看看它是如何包裝原始協議的。
我們來安裝該庫:
yarn add chrome-remote-interface
例子 - 列印用戶代理:
const CDP = require('chrome-remote-interface');
...
launchChrome().then(async chrome => {
const version = await CDP.Version({port: chrome.port});
console.log(version['User-Agent']);
});
結果是類似這樣的東西:HeadlessChrome/60.0.3082.0。
例子 - 檢查網站是否有 Web 應用程序清單:
const CDP = require('chrome-remote-interface');
...
(async function() {
const chrome = await launchChrome();
const protocol = await CDP({port: chrome.port});
// Extract the DevTools protocol domains we need and enable them.
// See API docs: https://chromedevtools.github.io/devtools-protocol/
const {Page} = protocol;
await Page.enable();
Page.navigate({url: 'https://www.chromestatus.com/'});
// Wait for window.onload before doing stuff.
Page.loadEventFired(async () => {
const manifest = await Page.getAppManifest();
if (manifest.url) {
console.log('Manifest: ' + manifest.url);
console.log(manifest.data);
} else {
console.log('Site has no app manifest');
}
protocol.close();
chrome.kill(); // Kill Chrome.
});
})();
例子 - 使用 DOM API 提取頁面的 <title>:
const CDP = require('chrome-remote-interface');
...
(async function() {
const chrome = await launchChrome();
const protocol = await CDP({port: chrome.port});
// Extract the DevTools protocol domains we need and enable them.
// See API docs: https://chromedevtools.github.io/devtools-protocol/
const {Page, Runtime} = protocol;
await Promise.all([Page.enable(), Runtime.enable()]);
Page.navigate({url: 'https://www.chromestatus.com/'});
// Wait for window.onload before doing stuff.
Page.loadEventFired(async () => {
const js = "document.querySelector('title').textContent";
// Evaluate the JS expression in the page.
const result = await Runtime.evaluate({expression: js});
console.log('Title of page: ' + result.result.value);
protocol.close();
chrome.kill(); // Kill Chrome.
});
})();
使用 Selenium、WebDriver 和 ChromeDriver
現在,Selenium 開啟了 Chrome 的完整實例。換句話說,這是一個自動化的解決方案,但不是完全無需顯示的。但是,Selenium 只需要進行小小的配置即可運行 Headless Chrome。如果你想要關於如何自己設置的完整說明,我建議你閱讀「使用 Headless Chrome 來運行 Selenium」,不過你可以從下面的一些示例開始。
使用 ChromeDriver
ChromeDriver 2.3.0 支持 Chrome 59 及更新版本,可與 Headless Chrome 配合使用。在某些情況下,你可能需要等到 Chrome 60 以解決 bug。例如,Chrome 59 中屏幕截圖已知存在問題。
安裝:
yarn add selenium-webdriver chromedriver
例子:
const fs = require('fs');
const webdriver = require('selenium-webdriver');
const chromedriver = require('chromedriver');
// This should be the path to your Canary installation.
// I'm assuming Mac for the example.
const PATH_TO_CANARY = '/Applications/Google Chrome Canary.app/Contents/MacOS/Google Chrome Canary';
const chromeCapabilities = webdriver.Capabilities.chrome();
chromeCapabilities.set('chromeOptions', {
binary: PATH_TO_CANARY // Screenshots require Chrome 60. Force Canary.
'args': [
'--headless',
]
});
const driver = new webdriver.Builder()
.forBrowser('chrome')
.withCapabilities(chromeCapabilities)
.build();
// Navigate to google.com, enter a search.
driver.get('https://www.google.com/');
driver.findElement({name: 'q'}).sendKeys('webdriver');
driver.findElement({name: 'btnG'}).click();
driver.wait(webdriver.until.titleIs('webdriver - Google Search'), 1000);
// Take screenshot of results page. Save to disk.
driver.takeScreenshot().then(base64png => {
fs.writeFileSync('screenshot.png', new Buffer(base64png, 'base64'));
});
driver.quit();
使用 WebDriverIO
WebDriverIO 是一個在 Selenium WebDrive 上構建的更高層次的 API。
安裝:
yarn add webdriverio chromedriver
例子:過濾 chromestatus.com 上的 CSS 功能:
const webdriverio = require('webdriverio');
const chromedriver = require('chromedriver');
// This should be the path to your Canary installation.
// I'm assuming Mac for the example.
const PATH_TO_CANARY = '/Applications/Google Chrome Canary.app/Contents/MacOS/Google Chrome Canary';
const PORT = 9515;
chromedriver.start([
'--url-base=wd/hub',
`--port=${PORT}`,
'--verbose'
]);
(async () => {
const opts = {
port: PORT,
desiredCapabilities: {
browserName: 'chrome',
chromeOptions: {
binary: PATH_TO_CANARY // Screenshots require Chrome 60. Force Canary.
args: ['--headless']
}
}
};
const browser = webdriverio.remote(opts).init();
await browser.url('https://www.chromestatus.com/features');
const title = await browser.getTitle();
console.log(`Title: ${title}`);
await browser.waitForText('.num-features', 3000);
let numFeatures = await browser.getText('.num-features');
console.log(`Chrome has ${numFeatures} total features`);
await browser.setValue('input[type="search"]', 'CSS');
console.log('Filtering features...');
await browser.pause(1000);
numFeatures = await browser.getText('.num-features');
console.log(`Chrome has ${numFeatures} CSS features`);
const buffer = await browser.saveScreenshot('screenshot.png');
console.log('Saved screenshot...');
chromedriver.stop();
browser.end();
})();
更多資源
以下是一些可以帶你入門的有用資源:
文檔
- DevTools Protocol Viewer - API 參考文檔
工具
- chrome-remote-interface - 基於 DevTools 協議的 node 模塊
- Lighthouse - 測試 Web 應用程序質量的自動化工具;大量使用了協議
- chrome-launcher - 用於啟動 Chrome 的 node 模塊,可以自動化
樣例
- "The Headless Web" - Paul Kinlan 發布的使用了 Headless 和 api.ai 的精彩博客
常見問題
我需要 --disable-gpu 標誌嗎?
目前是需要的。--disable-gpu 標誌在處理一些 bug 時是需要的。在未來版本的 Chrome 中就不需要了。查看 https://crbug.com/546953#c152 和 https://crbug.com/695212 獲取更多信息。
所以我仍然需要 Xvfb 嗎?
不。Headless Chrome 不使用窗口,所以不需要像 Xvfb 這樣的顯示伺服器。沒有它你也可以愉快地運行你的自動化測試。
什麼是 Xvfb?Xvfb 是一個用於類 Unix 系統的運行於內存之內的顯示伺服器,可以讓你運行圖形應用程序(如 Chrome),而無需附加的物理顯示器。許多人使用 Xvfb 運行早期版本的 Chrome 進行 「headless」 測試。
如何創建一個運行 Headless Chrome 的 Docker 容器?
查看 lighthouse-ci。它有一個使用 Ubuntu 作為基礎鏡像的 Dockerfile 示例,並且在 App Engine Flexible 容器中安裝和運行了 Lighthouse。
我可以把它和 Selenium / WebDriver / ChromeDriver 一起使用嗎?
是的。查看 Using Selenium, WebDrive, or ChromeDriver。
它和 PhantomJS 有什麼關係?
Headless Chrome 和 PhantomJS 是類似的工具。它們都可以用來在無需顯示的環境中進行自動化測試。兩者的主要不同在於 Phantom 使用了一個較老版本的 WebKit 作為它的渲染引擎,而 Headless Chrome 使用了最新版本的 Blink。
目前,Phantom 提供了比 DevTools protocol 更高層次的 API。
我在哪兒提交 bug?
對於 Headless Chrome 的 bug,請提交到 crbug.com。
對於 DevTools 協議的 bug,請提交到 github.com/ChromeDevTools/devtools-protocol。
作者簡介
Eric Bidelman 谷歌工程師,Lighthouse 開發,Web 和 Web 組件開發,Chrome 開發
via: https://developers.google.com/web/updates/2017/04/headless-chrome
作者:Eric Bidelman 譯者:firmianay 校對:wxy
本文轉載來自 Linux 中國: https://github.com/Linux-CN/archive