用 Python 繪製數據的7種最流行的方法

比較七個在 Python 中繪圖的庫和 API,看看哪個最能滿足你的需求。
「如何在 Python 中繪圖?」曾經這個問題有一個簡單的答案:Matplotlib 是唯一的辦法。如今,Python 作為數據科學的語言,有著更多的選擇。你應該用什麼呢?
本指南將幫助你決定。
它將向你展示如何使用四個最流行的 Python 繪圖庫:Matplotlib、Seaborn、Plotly 和 Bokeh,再加上兩個值得考慮的優秀的後起之秀:Altair,擁有豐富的 API;Pygal,擁有漂亮的 SVG 輸出。我還會看看 Pandas 提供的非常方便的繪圖 API。
對於每一個庫,我都包含了源代碼片段,以及一個使用 Anvil 的完整的基於 Web 的例子。Anvil 是我們的平台,除了 Python 之外,什麼都不用做就可以構建網路應用。讓我們一起來看看。
示例繪圖
每個庫都採取了稍微不同的方法來繪製數據。為了比較它們,我將用每個庫繪製同樣的圖,並給你展示源代碼。對於示例數據,我選擇了這張 1966 年以來英國大選結果的分組柱狀圖。
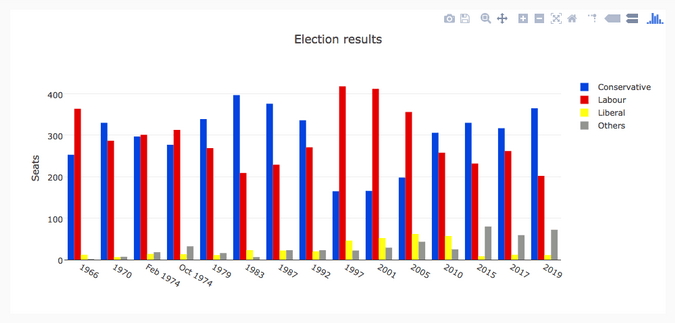
我從維基百科上整理了英國選舉史的數據集:從 1966 年到 2019 年,保守黨、工黨和自由黨(廣義)在每次選舉中贏得的英國議會席位數,加上「其他」贏得的席位數。你可以以 CSV 文件格式下載它。
Matplotlib
Matplotlib 是最古老的 Python 繪圖庫,現在仍然是最流行的。它創建於 2003 年,是 SciPy Stack 的一部分,SciPy Stack 是一個類似於 Matlab 的開源科學計算庫。
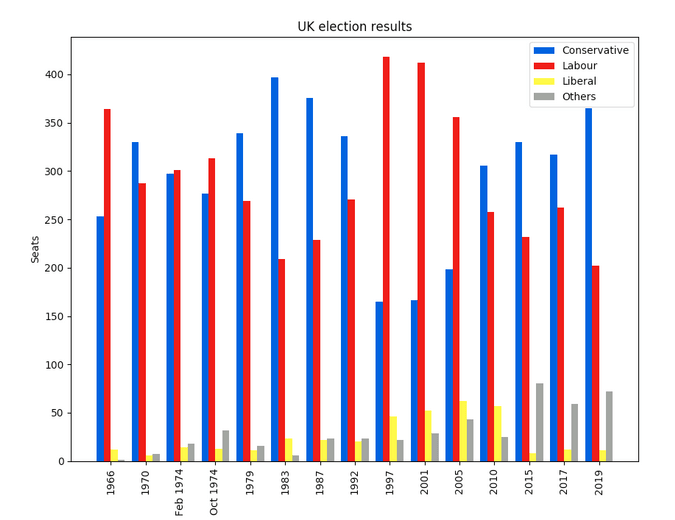
Matplotlib 為你提供了對繪製的精確控制。例如,你可以在你的條形圖中定義每個條形圖的單獨的 X 位置。下面是繪製這個圖表的代碼(你可以在這裡運行):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from votes import wide as df
# Initialise a figure. subplots() with no args gives one plot.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# A little data preparation
years = df['year']
x = np.arange(len(years))
# Plot each bar plot. Note: manually calculating the 'dodges' of the bars
ax.bar(x - 3*width/2, df['conservative'], width, label='Conservative', color='#0343df')
ax.bar(x - width/2, df['labour'], width, label='Labour', color='#e50000')
ax.bar(x + width/2, df['liberal'], width, label='Liberal', color='#ffff14')
ax.bar(x + 3*width/2, df['others'], width, label='Others', color='#929591')
# Customise some display properties
ax.set_ylabel('Seats')
ax.set_title('UK election results')
ax.set_xticks(x) # This ensures we have one tick per year, otherwise we get fewer
ax.set_xticklabels(years.astype(str).values, rotation='vertical')
ax.legend()
# Ask Matplotlib to show the plot
plt.show()這是用 Matplotlib 繪製的選舉結果:
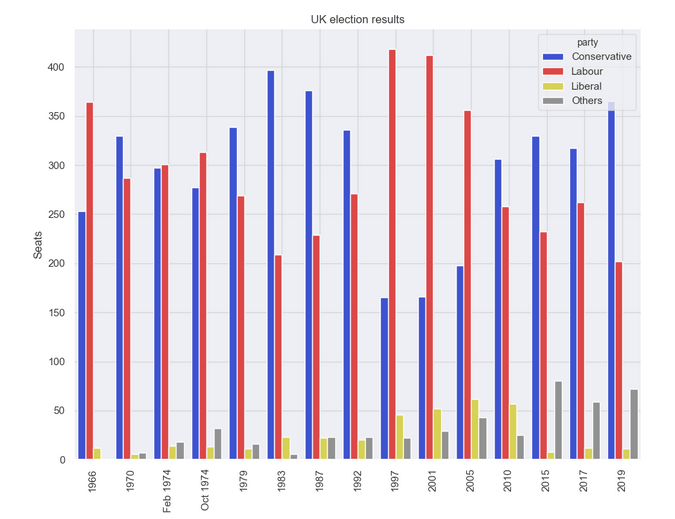
Seaborn
Seaborn 是 Matplotlib 之上的一個抽象層;它提供了一個非常整潔的界面,讓你可以非常容易地製作出各種類型的有用繪圖。
不過,它並沒有在能力上有所妥協!Seaborn 提供了訪問底層 Matplotlib 對象的逃生艙口,所以你仍然可以進行完全控制。
Seaborn 的代碼比原始的 Matplotlib 更簡單(可在此處運行):
import seaborn as sns
from votes import long as df
# Some boilerplate to initialise things
sns.set()
plt.figure()
# This is where the actual plot gets made
ax = sns.barplot(data=df, x="year", y="seats", hue="party", palette=['blue', 'red', 'yellow', 'grey'], saturation=0.6)
# Customise some display properties
ax.set_title('UK election results')
ax.grid(color='#cccccc')
ax.set_ylabel('Seats')
ax.set_xlabel(None)
ax.set_xticklabels(df["year"].unique().astype(str), rotation='vertical')
# Ask Matplotlib to show it
plt.show()並生成這樣的圖表:
Plotly
Plotly 是一個繪圖生態系統,它包括一個 Python 繪圖庫。它有三個不同的介面:
- 一個面向對象的介面。
- 一個命令式介面,允許你使用類似 JSON 的數據結構來指定你的繪圖。
- 類似於 Seaborn 的高級介面,稱為 Plotly Express。
Plotly 繪圖被設計成嵌入到 Web 應用程序中。Plotly 的核心其實是一個 JavaScript 庫!它使用 D3 和 stack.gl 來繪製圖表。
你可以通過向該 JavaScript 庫傳遞 JSON 來構建其他語言的 Plotly 庫。官方的 Python 和 R 庫就是這樣做的。在 Anvil,我們將 Python Plotly API 移植到了 Web 瀏覽器中運行。
這是使用 Plotly 的源代碼(你可以在這裡運行):
import plotly.graph_objects as go
from votes import wide as df
# Get a convenient list of x-values
years = df['year']
x = list(range(len(years)))
# Specify the plots
bar_plots = [
go.Bar(x=x, y=df['conservative'], name='Conservative', marker=go.bar.Marker(color='#0343df')),
go.Bar(x=x, y=df['labour'], name='Labour', marker=go.bar.Marker(color='#e50000')),
go.Bar(x=x, y=df['liberal'], name='Liberal', marker=go.bar.Marker(color='#ffff14')),
go.Bar(x=x, y=df['others'], name='Others', marker=go.bar.Marker(color='#929591')),
]
# Customise some display properties
layout = go.Layout(
title=go.layout.Title(text="Election results", x=0.5),
yaxis_title="Seats",
xaxis_tickmode="array",
xaxis_tickvals=list(range(27)),
xaxis_ticktext=tuple(df['year'].values),
)
# Make the multi-bar plot
fig = go.Figure(data=bar_plots, layout=layout)
# Tell Plotly to render it
fig.show()選舉結果圖表:

Bokeh
Bokeh(發音為 「BOE-kay」)擅長構建互動式繪圖,所以這個標準的例子並沒有將其展現其最好的一面。和 Plotly 一樣,Bokeh 的繪圖也是為了嵌入到 Web 應用中,它以 HTML 文件的形式輸出繪圖。
下面是使用 Bokeh 的代碼(你可以在這裡運行):
from bokeh.io import show, output_file
from bokeh.models import ColumnDataSource, FactorRange, HoverTool
from bokeh.plotting import figure
from bokeh.transform import factor_cmap
from votes import long as df
# Specify a file to write the plot to
output_file("elections.html")
# Tuples of groups (year, party)
x = [(str(r[1]['year']), r[1]['party']) for r in df.iterrows()]
y = df['seats']
# Bokeh wraps your data in its own objects to support interactivity
source = ColumnDataSource(data=dict(x=x, y=y))
# Create a colourmap
cmap = {
'Conservative': '#0343df',
'Labour': '#e50000',
'Liberal': '#ffff14',
'Others': '#929591',
}
fill_color = factor_cmap('x', palette=list(cmap.values()), factors=list(cmap.keys()), start=1, end=2)
# Make the plot
p = figure(x_range=FactorRange(*x), width=1200, title="Election results")
p.vbar(x='x', top='y', width=0.9, source=source, fill_color=fill_color, line_color=fill_color)
# Customise some display properties
p.y_range.start = 0
p.x_range.range_padding = 0.1
p.yaxis.axis_label = 'Seats'
p.xaxis.major_label_orientation = 1
p.xgrid.grid_line_color = None圖表如下:

Altair
Altair 是基於一種名為 Vega 的聲明式繪圖語言(或「可視化語法」)。這意味著它具有經過深思熟慮的 API,可以很好地擴展複雜的繪圖,使你不至於在嵌套循環的地獄中迷失方向。
與 Bokeh 一樣,Altair 將其圖形輸出為 HTML 文件。這是代碼(你可以在這裡運行):
import altair as alt
from votes import long as df
# Set up the colourmap
cmap = {
'Conservative': '#0343df',
'Labour': '#e50000',
'Liberal': '#ffff14',
'Others': '#929591',
}
# Cast years to strings
df['year'] = df['year'].astype(str)
# Here's where we make the plot
chart = alt.Chart(df).mark_bar().encode(
x=alt.X('party', title=None),
y='seats',
column=alt.Column('year', sort=list(df['year']), title=None),
color=alt.Color('party', scale=alt.Scale(domain=list(cmap.keys()), range=list(cmap.values())))
)
# Save it as an HTML file.
chart.save('altair-elections.html')結果圖表:

Pygal
Pygal 專註於視覺外觀。它默認生成 SVG 圖,所以你可以無限放大它們或列印出來,而不會被像素化。Pygal 繪圖還內置了一些很好的交互性功能,如果你想在 Web 應用中嵌入繪圖,Pygal 是另一個被低估了的候選者。
代碼是這樣的(你可以在這裡運行它):
import pygal
from pygal.style import Style
from votes import wide as df
# Define the style
custom_style = Style(
colors=('#0343df', '#e50000', '#ffff14', '#929591')
font_family='Roboto,Helvetica,Arial,sans-serif',
background='transparent',
label_font_size=14,
)
# Set up the bar plot, ready for data
c = pygal.Bar(
title="UK Election Results",
style=custom_style,
y_title='Seats',
width=1200,
x_label_rotation=270,
)
# Add four data sets to the bar plot
c.add('Conservative', df['conservative'])
c.add('Labour', df['labour'])
c.add('Liberal', df['liberal'])
c.add('Others', df['others'])
# Define the X-labels
c.x_labels = df['year']
# Write this to an SVG file
c.render_to_file('pygal.svg')繪製結果:

Pandas
Pandas 是 Python 的一個極其流行的數據科學庫。它允許你做各種可擴展的數據處理,但它也有一個方便的繪圖 API。因為它直接在數據幀上操作,所以 Pandas 的例子是本文中最簡潔的代碼片段,甚至比 Seaborn 的代碼還要短!
Pandas API 是 Matplotlib 的一個封裝器,所以你也可以使用底層的 Matplotlib API 來對你的繪圖進行精細的控制。
這是 Pandas 中的選舉結果圖表。代碼精美簡潔!
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
from votes import wide as df
cmap = ListedColormap(['#0343df', '#e50000', '#ffff14', '#929591'])
ax = df.plot.bar(x='year', colormap=cmap)
ax.set_xlabel(None)
ax.set_ylabel('Seats')
ax.set_title('UK election results')
plt.show()繪圖結果:

要運行這個例子,請看這裡。
以你的方式繪製
Python 提供了許多繪製數據的方法,無需太多的代碼。雖然你可以通過這些方法快速開始創建你的繪圖,但它們確實需要一些本地配置。如果需要,Anvil 為 Python 開發提供了精美的 Web 體驗。祝你繪製愉快!
via: https://opensource.com/article/20/4/plot-data-python
作者:[Shaun Taylor-Morgan](https://opensource.com/users/shaun-taylor-morgan "View user profile.") 譯者:wxy 校對:wxy
本文轉載來自 Linux 中國: https://github.com/Linux-CN/archive