Linux 上使用 backup-manager 进行系统备份
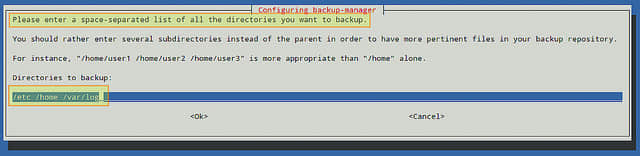
在下一步中,会询问你要备份的所有目录(用空格分隔)。建议,但不是严格要求,列出同一父目录中的几个子目录,而不要仅仅输入父目录。
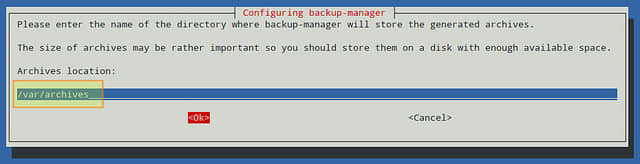
你可以跳过该步骤并在以后对配置文件中BM_TARBALL_DIRECTORIESb变量进行设置。否则的话,就请尽可能多地添加你想要的目录,然后选择OK:
Fedora或CentOS/RHEL
# yum install backup-manager
在CentOS/RHEL上,在运行以上yum命令前,你将需要先启用EPEL仓库。
配置备份管理器
备份管理器的主配置文件是/etc/backup-manager.conf。该文件被划分为几个章节,里面定义了备份方法和相关的变量(或“键值”),这些配置让备份管理器成为一个多样化的工具,可以广泛地应付各种状况。
出于演示目的,我们将考虑以下环境:
- 每周对/etc,/home以及/var/log目录进行一次完整备份(我们将在下面通过cron设置备份的频率)。
- 通过SSH传输.tar.gz备份归档文件到两台不同主机dev1和dev3上指定的目标目录。
- 通过SSH备份本地MySQL数据库到相同目标主机。
用你喜爱的文本编辑器打开/etc/backup-manager.conf文件,并编辑以下变量。如果你愿意,你大可不必理会那些#开头的行。在本文中,它只是用作说明的注释:
# Specify the backup method(s) that will be used.
# tarball: takes a list of directories and builds the corresponding tarballs.
# mysql: archives MySQL databases using mysqldump. To restore the database, you # need to use the same tool manually.
export BM_ARCHIVE_METHOD="tarball mysql"
# Where to store the backups.
export BM_REPOSITORY_ROOT="/var/archives"
# The following directive indicates backup-manager to name
# the generated files after the directory that was backed up.
export BM_TARBALL_NAMEFORMAT="long"
# Define the compression type for the generated files.
export BM_TARBALL_FILETYPE="tar.gz"
# List the directories that you want to backup.
export BM_TARBALL_DIRECTORIES="/etc /home /var/log"
# Exclude some subdirectories or file extensions.
export BM_TARBALL_BLACKLIST="/var/log/myotherapp.log *.mp3 *.mp4"
# List the database(s) that you want to backup, separated by spaces.
export BM_MYSQL_DATABASES="mysql mybase wordpress dotclear phpbb2"
# MySQL username.
export BM_MYSQL_ADMINLOGIN="root"
# MySQL password for username.
export BM_MYSQL_ADMINPASS="mypassword"
# Add support for DROP statements (optional).
export BM_MYSQL_SAFEDUMPS="true"
# The hostname or IP address where the database(s) reside.
export BM_MYSQL_HOST="localhost"
# Port where MySQL server is listening.
export BM_MYSQL_PORT="3306"
# Compression type (optional).
export BM_MYSQL_FILETYPE="gzip"
# Do not archive remote hosts, but only localhost.
BM_TARBALL_OVER_SSH="false"
# User account for SSH upload.
export BM_UPLOAD_SSH_USER="root"
# Absolute path of the user's private key for passwordless SSH login.
export BM_UPLOAD_SSH_KEY="/root/.ssh/id_rsa"
# Remote hosts (make sure you have exported your public key to them):
export BM_UPLOAD_SSH_HOSTS="dev1 dev3"
# Remote destination for uploading backups. If it doesn't exist,
# this directory will be created automatically the first time
# backup-manager runs.
export BM_UPLOAD_SSH_DESTINATION="/var/archives/backups/$HOSTNAME"
运行备份管理器
要手动运行备份管理器,请输入以下命令。你也可以选择添加‘-v’标识以便一步一步详细检查运行过程。
# backup-manager
BM_TARBALL_DIRECTORIES列出的目录将作为tarball备份到BM_REPOSITORY_ROOT目录,然后通过SSH传输到BM_UPLOAD_SSH_DESTINATION指定的主机dev1和dev3。
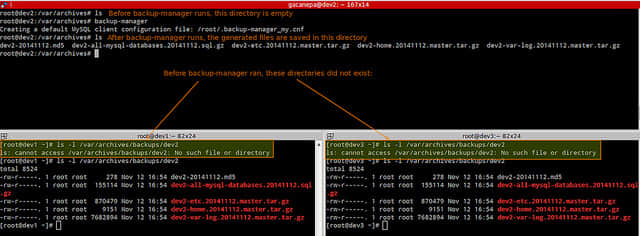
正如你在上面图片中看到的那样,备份管理器在运行的时候创建了一个名为/root/.back-manager_my.cnf的文件,MySQL密码通过BM_MYSQL_ADMINPASS指定。那样,mysqldump可以验证到MySQL服务器,而不必在命令行以明文格式接受密码,那样会有安全风险。
通过cron运行备份管理器
一旦决定哪一天是进行每周备份的最佳日子(最佳时间),你可以让cron来为你运行备份管理器。
打开root的crontab文件(注意,你必须以root登录):
# crontab -e
假定你想要在星期天的上午5:15分运行备份管理器,那么就添加下面这行。
15 05 * * 0 /usr/sbin/backup-manager > /dev/null 2>&1
小结
在本文中,我已经展示了备份管理器这个备份工具是怎样的简单而强大,并且易于使用。在你的备份策略中,你可能还有其它几个选项需要考虑,请参阅手册页或用户手册,里面也包含了几个部署实例和建议。
希望此文对你有所帮助,请在下面随意提问和评论。
via: http://xmodulo.com/linux-backup-manager.html
作者:Gabriel Cánepa 译者:GOLinux 校对:wxy
本文转载来自 Linux 中国: https://github.com/Linux-CN/archive