如何配置 fail2ban 来保护 Apache 服务器

让我们更深入地了解 fail2ban 监狱。监狱定义了具体的应用策略,它会为指定的程序触发一个保护措施。fail2ban在 /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf 下为一些流行程序如Apache、Dovecot、Lighttpd、MySQL、Postfix、SSH 等预定义了一些监狱。每个监狱都通过特定的程序日志过滤器(在/etc/fail2ban/fileter.d 下面)来检测通常的攻击。让我看一个例子监狱:SSH监狱。
[ssh]
enabled = true
port = ssh
filter = sshd
logpath = /var/log/auth.log
maxretry = 6
banaction = iptables-multiport
SSH监狱的配置定义了这些参数:
- [ssh]: 方括号内是监狱的名字。
- enabled:是否启用监狱
- port: 端口号(或者对应的服务名称)
- filter: 检测攻击的日志解析规则
- logpath: 所检测的日志文件
- maxretry: 最大失败次数
- banaction: 所进行的禁止操作
定义在监狱配置中的任意参数都会覆盖fail2ban-wide 中相应的默认配置参数。相反,任何缺少的参数都会使用定义在[DEFAULT] 字段的默认值。
预定义的日志过滤器都放在/etc/fail2ban/filter.d,而可以采取的禁止操作放在 /etc/fail2ban/action.d。
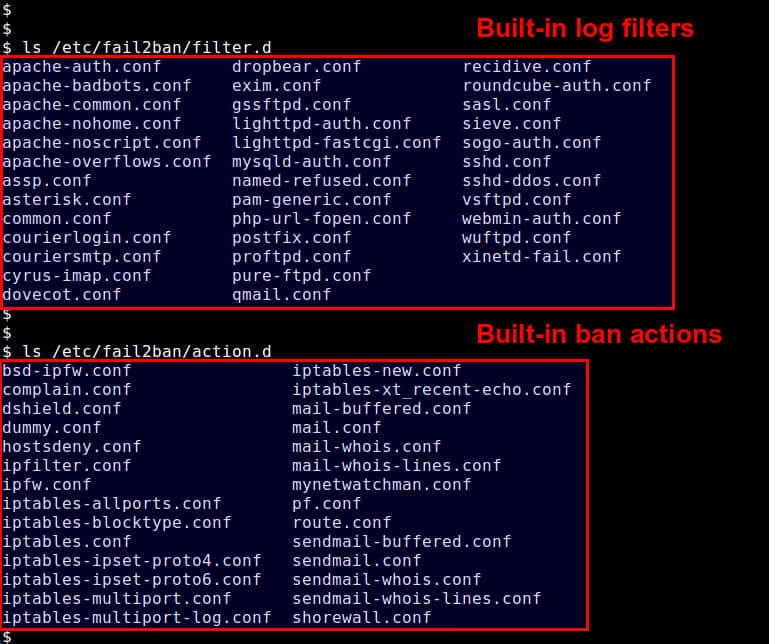
如果你想要覆盖fail2ban的默认操作或者定义任何自定义监狱,你可以创建*/etc/fail2ban/jail.local**文件。本篇教程中,我会使用/etc/fail2ban/jail.local。
启用预定义的apache监狱
fail2ban的默认安装为Apache服务提供了一些预定义监狱和过滤器。我要启用这些内建的Apache监狱。由于Debian和RedHat配置的稍微不同,我会分别提供它们的配置文件。
在Debian 或者 Ubuntu启用Apache监狱
要在基于Debian的系统上启用预定义的apache监狱,如下创建/etc/fail2ban/jail.local。
$ sudo vi /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
# 检测密码认证失败
[apache]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = apache-auth
logpath = /var/log/apache*/*error.log
maxretry = 6
# 检测漏洞和 PHP 脆弱性扫描
[apache-noscript]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = apache-noscript
logpath = /var/log/apache*/*error.log
maxretry = 6
# 检测 Apache 溢出攻击
[apache-overflows]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = apache-overflows
logpath = /var/log/apache*/*error.log
maxretry = 2
# 检测在服务器寻找主目录的尝试
[apache-nohome]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = apache-nohome
logpath = /var/log/apache*/*error.log
maxretry = 2
由于上面的监狱没有指定措施,这些监狱都将会触发默认的措施。要查看默认的措施,在/etc/fail2ban/jail.conf中的[DEFAULT]下找到“banaction”。
banaction = iptables-multiport
本例中,默认的操作是iptables-multiport(定义在/etc/fail2ban/action.d/iptables-multiport.conf)。这个措施使用iptable的多端口模块禁止一个IP地址。
在启用监狱后,你必须重启fail2ban来加载监狱。
$ sudo service fail2ban restart
在CentOS/RHEL 或者 Fedora中启用Apache监狱
要在基于红帽的系统中启用预定义的监狱,如下创建/etc/fail2ban/jail.local。
$ sudo vi /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
# 检测密码认证失败
[apache]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = apache-auth
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
maxretry = 6
# 检测抓取邮件地址的爬虫
[apache-badbots]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = apache-badbots
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*access_log
bantime = 172800
maxretry = 1
# 检测漏洞和 PHP 脆弱性扫描
[apache-noscript]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = apache-noscript
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
maxretry = 6
# 检测 Apache 溢出攻击
[apache-overflows]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = apache-overflows
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
maxretry = 2
# 检测在服务器寻找主目录的尝试
[apache-nohome]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = apache-nohome
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
maxretry = 2
# 检测执行不存在的脚本的企图
# 这些都是流行的网站服务程序
# 如:webmail, phpMyAdmin,WordPress
port = http,https
filter = apache-botsearch
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
maxretry = 2
注意这些监狱文件默认的操作是iptables-multiport(定义在/etc/fail2ban/jail.conf中[DEFAULT]字段下的“banaction”中)。这个措施使用iptable的多端口模块禁止一个IP地址。
启用监狱后,你必须重启fail2ban来加载监狱。
在 Fedora 或者 CentOS/RHEL 7中:
$ sudo systemctl restart fail2ban
在 CentOS/RHEL 6中:
$ sudo service fail2ban restart
检查和管理fail2ban禁止状态
监狱一旦激活后,你可以用fail2ban的客户端命令行工具来监测当前的禁止状态。
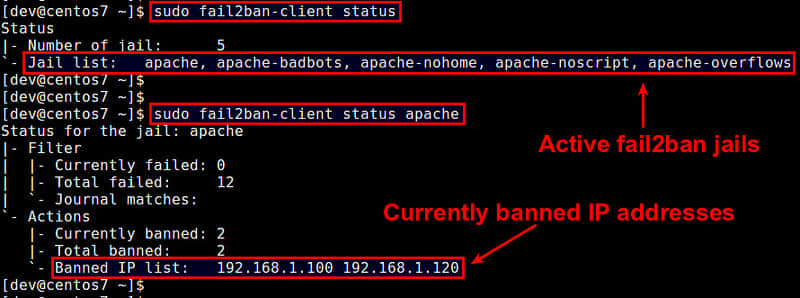
查看激活的监狱列表:
$ sudo fail2ban-client status
查看特定监狱的状态(包含禁止的IP列表):
$ sudo fail2ban-client status [监狱名]
你也可以手动禁止或者解禁IP地址:
要用制定监狱禁止IP:
$ sudo fail2ban-client set [name-of-jail] banip [ip-address]
要解禁指定监狱屏蔽的IP:
$ sudo fail2ban-client set [name-of-jail] unbanip [ip-address]
总结
本篇教程解释了fail2ban监狱如何工作以及如何使用内置的监狱来保护Apache服务器。依赖于你的环境以及要保护的web服务器类型,你或许要调整已有的监狱或者编写自定义监狱和日志过滤器。查看outfail2ban的官方Github页面来获取最新的监狱和过滤器示例。
你有在生产环境中使用fail2ban么?分享一下你的经验吧。
via: http://xmodulo.com/configure-fail2ban-apache-http-server.html
本文转载来自 Linux 中国: https://github.com/Linux-CN/archive